Thank you! We will contact you shortly.
Contact Us
Source Code Linking
Purpose
Linking a source code repository to a subsystem enables Reqode to keep requirements and implementation aligned and unlocks AI-assisted development workflows.
Where to find in UI
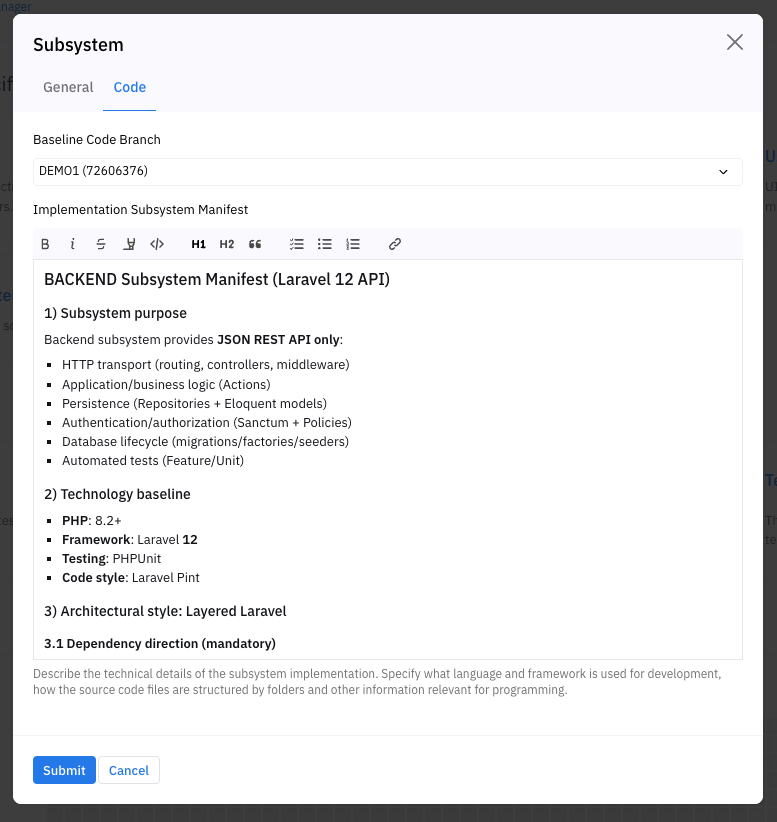
- Project Settings → Subsystems → (… → Edit) → Code tab
Prerequisites
- User is a member of the project.
- Permissions scope: Project Settings.
- A repository integration is configured (GitHub/GitLab/Bitbucket, etc.).
- Initial repository synchronization has been completed.
Note: The Source Code Repository field is shown only when integration is configured and synced.
Step-by-step
TL;DR (happy path)
- Make sure repository integration is configured and synced.
- Open Project Settings → Subsystems.
- Open the subsystem editor (… → Edit).
- Go to the Code tab.
- Select Source Code Repository.
- Click Submit.
Detailed explanation
Linking a source code repository to a subsystem enables the most powerful capabilities of Reqode by establishing a direct, continuous connection between requirements and code.
Once linked, the subsystem becomes an active participant in AI-assisted development and analysis workflows.
Why Link Source Code to a Subsystem
Source code linking enables the following core capabilities:
- AI Code Generation Generate implementation code based on subsystem requirements and development manifests.
- Analysis of Existing Code to Derive Requirements Analyze the current codebase to identify functionality, gaps, and implicit requirements.
- Continuous Requirements–Code Alignment Perform ongoing analysis, comparison, and correction of mismatches between:RequirementsArchitectureActual implementation
- Requirements
- Architecture
- Actual implementation
This ensures that requirements and code remain synchronized throughout the system lifecycle.
Prerequisites
Before linking source code to a subsystem, you must:
- Configure an integration with an external source code repository (e.g., Git-based repositories such as GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket)
- Perform the initial repository synchronization
Only after these steps will source code linking become available at the subsystem level.
Linking a Repository to a Subsystem
After the integration is configured and the first synchronization is completed:
- Open the Subsystem editor
- Navigate to the Code tab
- Select the repository that contains the source code for this subsystem
Once selected, the repository becomes the authoritative source of implementation for the subsystem.
Code Synchronization Behavior
After linking a repository:
- During the next synchronization, the system:
- Loads the subsystem source code
- Records the latest commit as the current code state
- After that:
- New commits are loaded on manual synchronization
- Or automatically, if a webhook is configured
Each synchronization updates the subsystem’s implementation state, enabling continuous analysis and alignment.
Impact on Subsystem Lifecycle
With source code linked:
- Subsystem versions can be correlated with actual code states
- Baselines can reference exact code commits
- AI-generated code respects existing implementation
- Architectural and requirement drift can be detected early
Source Code Linking turns a subsystem from a static definition into a living, continuously analyzed development unit.
Project Branches and Code Branch Mapping
Reqode supports parallel development by allowing you to work with project branches.
When project branches are used, each project branch can be linked to its own source code branch for the same subsystem.
This enables independent and concurrent evolution of:
- Requirements
- Architecture
- Implementation
within separate development streams.
How Branch Mapping Works
For each subsystem:
- The project branch defines the requirements and artifacts context
- The linked code branch defines the implementation context
This allows you to:
- Develop different features or versions in parallel
- Experiment without affecting the main branch
- Maintain long-lived release or maintenance branches
Example scenarios:
- main project branch → dev code branch
- feature-new-ui project branch → feature-new-ui code branch
Benefits of Branch-Level Code Linking
By mapping project branches to code branches, you can:
- Keep requirements and code aligned per branch
- Avoid mixing changes from different development streams
- Generate code that matches the correct branch context
- Analyze code changes relative to branch-specific requirements
- Safely manage parallel development and releases
Continuous Synchronization per Branch
When branch mapping is configured:
- Each project branch synchronizes only its linked code branch
- Commits are analyzed within the correct branch context
- AI-generated code respects the active branch configuration
This ensures that Reqode maintains branch-aware alignment between requirements and implementation.
Best Practices
- Use a stable mapping for long-lived branches (e.g., main, release)
- Create separate project branches for experimental or large changes
- Keep branch naming consistent between Reqode and the repository
- Avoid reusing the same code branch across unrelated project branches
Result
- The subsystem is linked to a repository.
- Future sync and AI workflows can use the subsystem implementation context.
Errors / Constraints
- If the integration is not configured/synced, the repository selector may not be available.
- If the repository is not accessible (permissions), linking may fail.
Best practices
- Link repositories early to enable continuous alignment.
- Keep repository ↔ subsystem mapping stable; avoid frequent switching.